HighVolumeHDF is Fresenius Medical Care
We want to make HighVolumeHDF available for all patients.
We are committed to supporting you for a seamless and reliable implementation with our specialised HighVolumeHDF product line and with dedicated support from our experts;
so that it feels like just pushing a button.

Percentage has been obtained from an internal calculation based on average treatment factors and at an Autoflow factor 1.2
Explore budget saving options, thanks to the ONLINEplus technology with dialysate savings features.
The 5008 CorDiax series and 6008 CAREsystem are equipped with the ONLINEplus technology, eliminating further requirements for the preparation and infusion of substitution fluid.
- AutoFlow automatically adjusts the dialysate flow rate to the effective blood flow rate during treatment
- Savings can be substantial for water, wastewater, concentrates, and energy, leading to cost reduction1,2
- EcoFlow reduces dialysate and energy consumption during preparation and after reinfusion
1 Mesic E, et al. Dialysate saving by automated control of flow rates: comparison between individualized online hemodiafiltration and standard hemodialysis. Hemodialysis International. 2011;15(4):522 9.
2 KultJ, StapfE. Changing emphasis in modern hemodialysis therapies: cost effectiveness of delivering higher doses of dialysis. The International Journal of Artificial Organs. 2007;30(7):577 82
Watch the video to learn more about these features:
Online production of substitution fluid makes HighVolumeHDF easy and efficient
- The preparation of sterile, non-pyrogenic and bicarbonate-buffered substitution fluid for HighVolumeHDF by ONLINEplus technology is based on a double-stage filtration process via DIASAFE®plus dialysis fluid filters and offers:
- No extra costs for an additional single-use filter
- No need for ready-made rinse solutions for priming, bolus or reinfusion with ONLINE fluid in all treatment modes
- Extensive amounts of substitution fluid for HDF available
- No waste bag needed due to rinse port
- The water quality for HighVolumeHDF has to meet the same international standards (ISO 23500-5) as for high-flux HD
- Fresenius Medical Care offers easy and reliable water quality management as part of a complete therapeutic system for HighVolumeHDF – technically advanced, affordable and sustainable
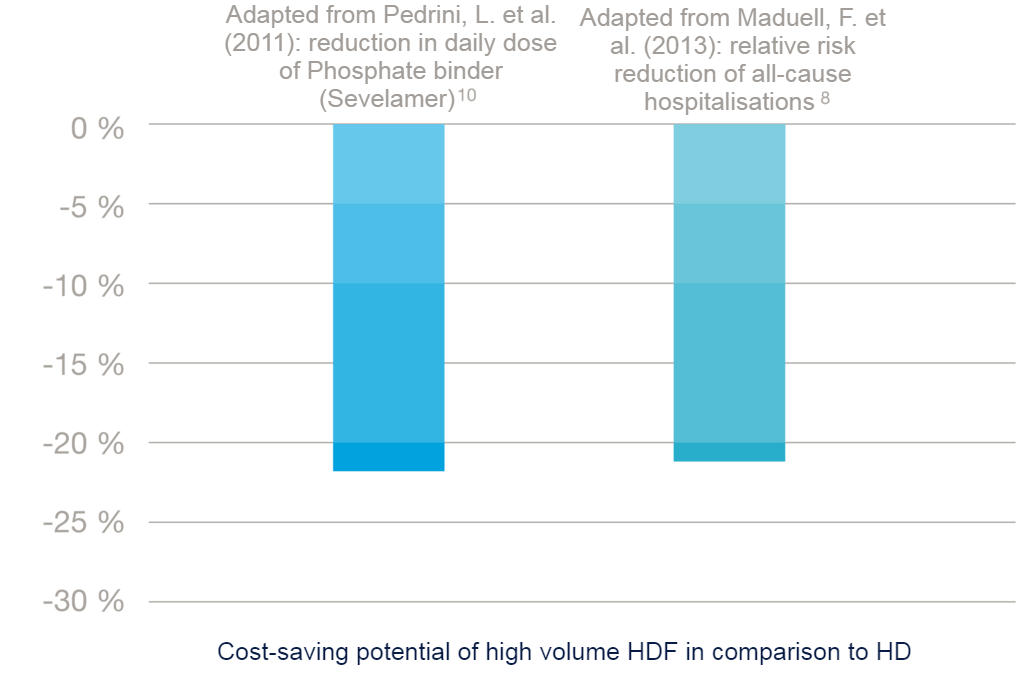
The main drivers of dialysis-related treatment costs are, in addition to direct procedure costs, hospitalisation, erythropoietin (EPO) and phosphate binder usage.10,11
In an economically tight environment, every opportunity to reduce the overall treatment cost should be examined. A high hospitalisation rate not only impacts patients' quality of life but is the most expensive form of medical care in every healthcare system.
Based on the ESHOL data, high-volume HDF has the potential to significantly reduce hospitalisation rates and hypotensive episodes.8 Some studies suggest that anemia correction may be facilitated in HDF-treated patients.7,10,11 Studies showed superior phosphate removal with HDF compared to standard HD, which may also result in better control of the phosphate level in the long term.10,28 Thus, higher quality of care has the potential to be provided at a lower medication burden and medication cost.
NICE (The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence) states that in-center HDF should be considered rather than in-center HD1,12
As per the NICE guidelines, it is suggested that HDF may have mortality benefits compared to standard HD and is more cost-effective.15
Delivering HD therapy in a cost-efficient and sustainable way

Improved clinical outcomes (i.e. Potential for increased survival and the potential for reduced medication requirements)
Offering therapy that is cost effective12,14

It is suggested that HDF may have mortality benefits compared to standard HD and is more cost-effective.15
HDF versus HD: Cost effectiveness analysis12,14-16
HDF considered as cost effective to HD
Reduced EPO requirements of up to 9 %14 with HDF based on weighted average calculation
Economic benefits for units using Fresenius Medical Care equipment as no switching costs from HD to HDF (including higher convection volumes), which means neutral budget impact
Fewer side effects for HDF compared to high-flux HD14
The NICE committee indicated additional benefit of HDF over high flux HD, the potential reduction in dialysis-related amyloidosis in patients on long term dialysis (for example more than 10 years)
Convection volume15
The NICE committee did not make any specific recommendation, but agreed that it was likely that patients who achieved higher convection volumes would get a greater benefit from HDF

Volume matters in hemodiafiltration
Automatically improve substitution volumes for HighVolumeHDF via AutoSub plus18
AutoSub plus – Insight and continuity make the difference
- To perform high-volume HDF, a dialysis machine should fulfill certain requirements.17 The 5008 series and the 6008 CAREsystem fulfill these prerequisites. Their sophisticated features enable the easy integration of HighVolumeHDF in daily clinical routines
- AutoSub plus automatically improves the substitution flow rates, thus allowing patient-individualised substitution volumes without additional user interaction. The basic principle of this approach is to avoid excessive hemoconcentration within the dialyser by continuously adapting the substitution flow18
- With AutoSub plus, HighVolumeHDF can be feasible in routine practice without additional workload and hemoconcentration-induced interruptions4
- It has been demonstrated that approximately 79% of HDF sessions can be achieved with HighVolumeHDF with AutoSub plus4
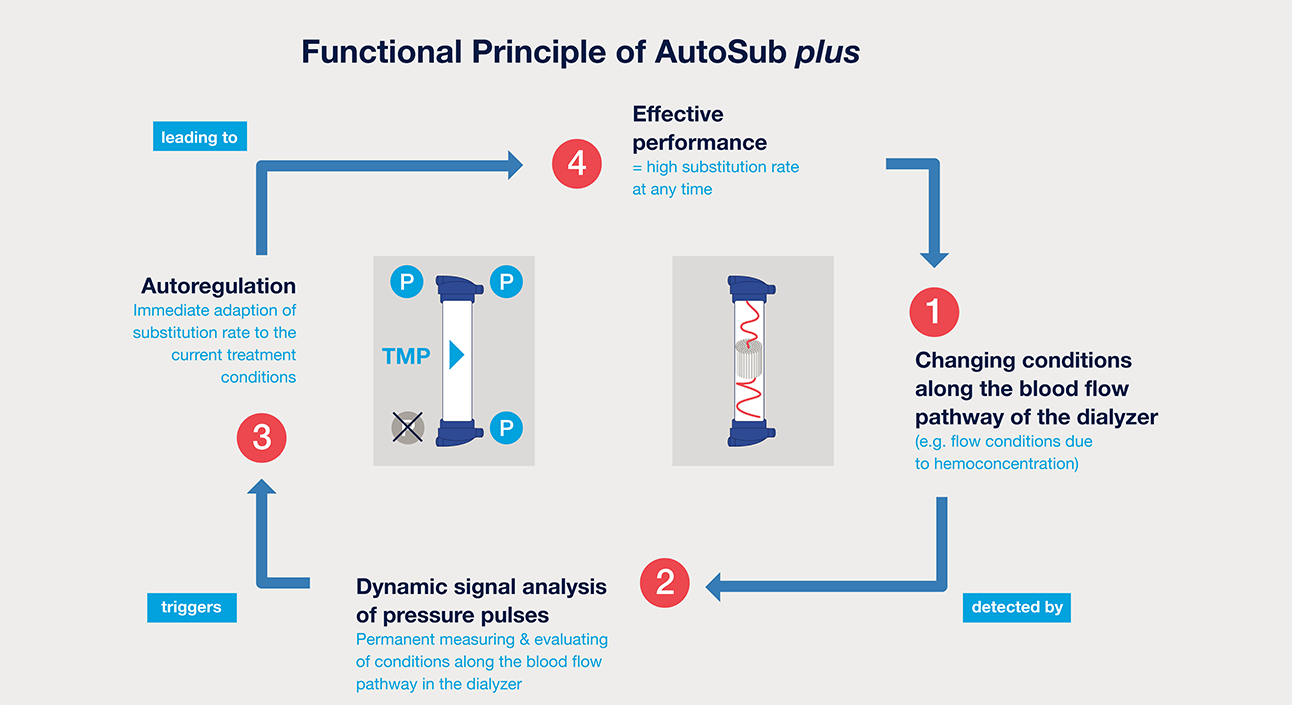
Functional principle of AutoSub plus19
- While other systems check and adjust the transmembrane pressure (TMP) at defined time intervals, AutoSub plus measures and evaluates the conditions directly inside the filter several times per minute. The innovative technology behind it is based on a dynamic signal analysis of pressure pulses. As a result, substitution volumes can be improved individually for every patient without any user interaction18
- Very precise information on the conditions in the dialyser is provided - not just across the membrane but also along the blood flow pathway
- Several checks per minute enable the continuous adaption of the substitution rates18
- The system is automatically activated at the start of treatment
- AutoSub plus supports the nephrologist in establishing HighVolumeHDF as standard therapy

HighVolumeHDF is easy to perform
HighVolumeHDF has become as simple and reliable as HD without any need for additional user interaction
ONLINEplus technology – Reducing workload, increasing usage
- An advanced therapy often means more complexity, more handling steps and an increased workload for healthcare professionals. But thanks to sophisticated products and technology from Fresenius Medical Care, the application of HighVolumeHDF in daily clinical routine has been greatly simplified4,18,20
- In addition, unique features such as AutoSub plus automatically improve substitution rates in post-dilution HDF and support the application of HighVolumeHDF4,18
- Our innovative blood lines are developed based on the idea that HighVolumeHDF should be as easy and safe to handle as HD. With a standard setup of a 5008S or 6008 CAREsystem, you can already perform HighVolumeHDF without additional preparations
- As a result, the application of HighVolumeHDF is not more complex or costly* than conventional HD. You can even switch from HD mode to HighVolumeHDF mode with the same equipment and disposables
* Cost should always be considered in the context of relevant local healthcare systems.
“Patients with dementia often do not understand the dialysis process. Sometimes they pull out the needle”.21
What if dialysis machines could feel the position of the venous needle?
If an alarm is emitted, the blood pump is stopped immediately, and the venous clamp is closed. This aims to give the nursing staff more time to react appropriately to critical pressure changes.
Safety features create confidence
In particular during high-volume HDF where high blood flows are aspired for, monitoring of the venous access is essential as blood loss would become critical within a very short time. The 5008 series and 6008 CAREsystem offer a sophisticated safety feature as standard in all machines that has been designed to reduce the risk of external blood loss:
- Venous Access Monitor (VAM) – if an alarm is emitted, the blood pump is stopped immediately, and the venous clamp is closed. This aims to give the nursing staff more time to react appropriately to critical pressure changes
- Blood line kinking and filter clotting monitoring (BLK) - Clotting and Kinking detection - Kinks in the tubing system might result in a mechanically generated hemolysis. The BLK function detects kinked tubing between the blood pump and the venous bubble catcher as well as clots beginning to develop in the dialyser, and issues a warning.
The innovative and highly automated features support nursing staff by streamlining daily workflows and support high and consistent levels of patient safety. The result is easy integration of high-volume HDF into daily routine.

FX dialysers designed for HighVolumeHDF
Hemodiafilters developed for improved middle molecule removal & albumin retention
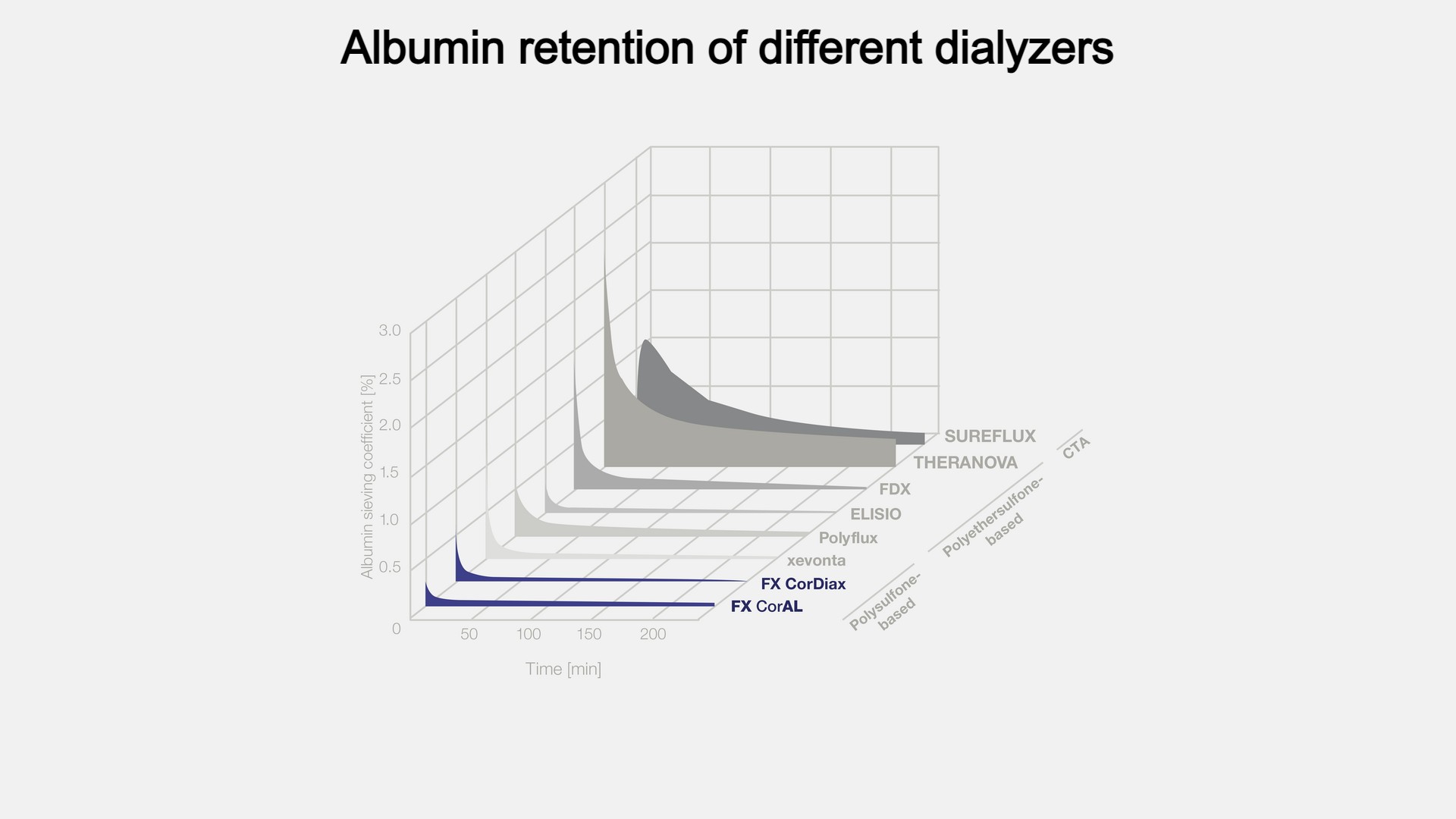
Graph adapted from Melchior et al., 2021, p. 623
Albumin retention capabilities of FX CorAL
Maintenance hemodialysis patients often experience increased protein catabolism, amino acid and albumin loss during dialysis, which contributes to malnutrition.
According to a study by Ehlerding et al., the albumin loss with FX CorAL 600 was less than 1.4 g during a typical HDF treatment of four hours.6
In another study by Melchior et al., FX CorAL was found to have the lowest albumin sieving coefficient decrease over time compared to other seven dialysers.
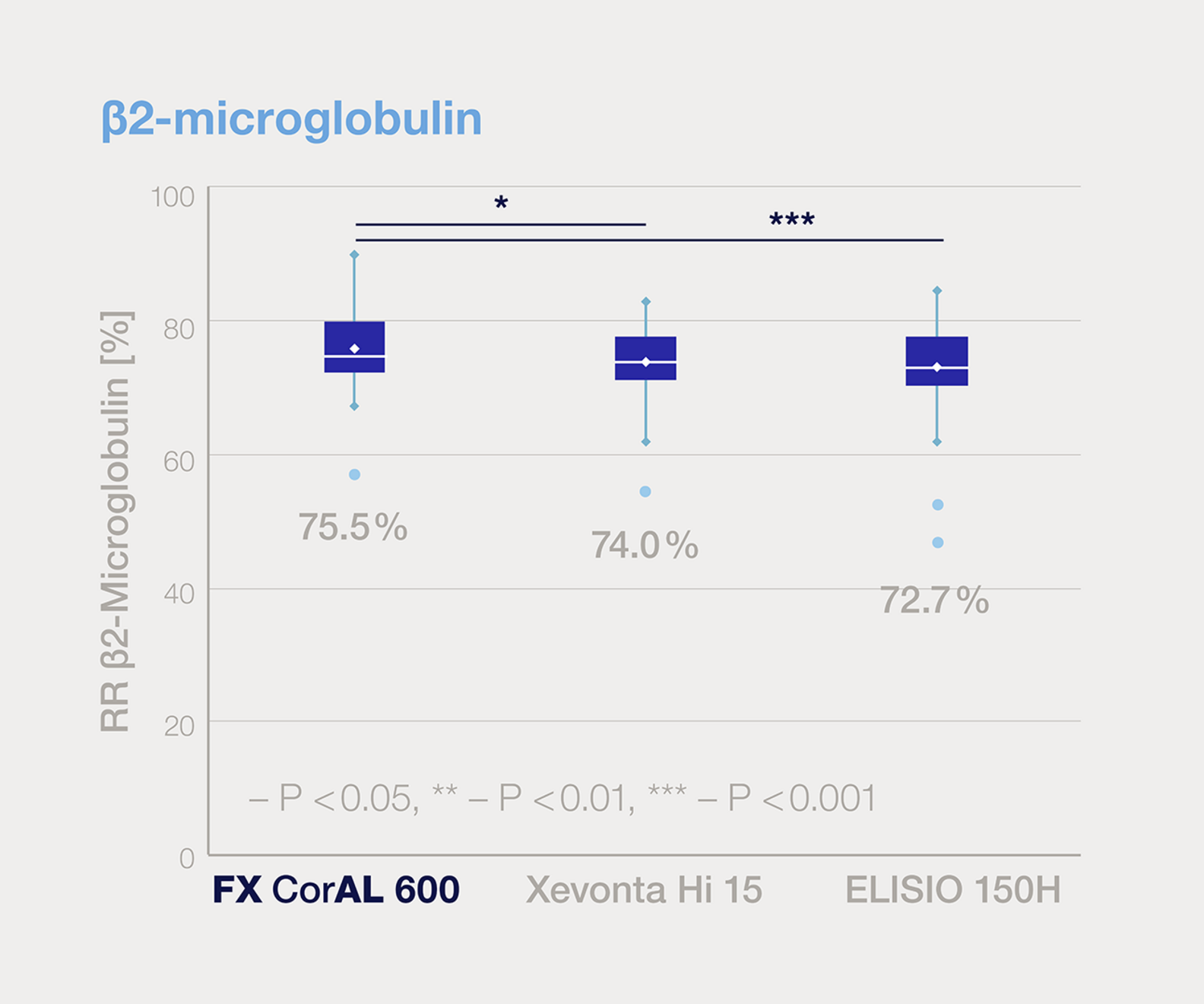
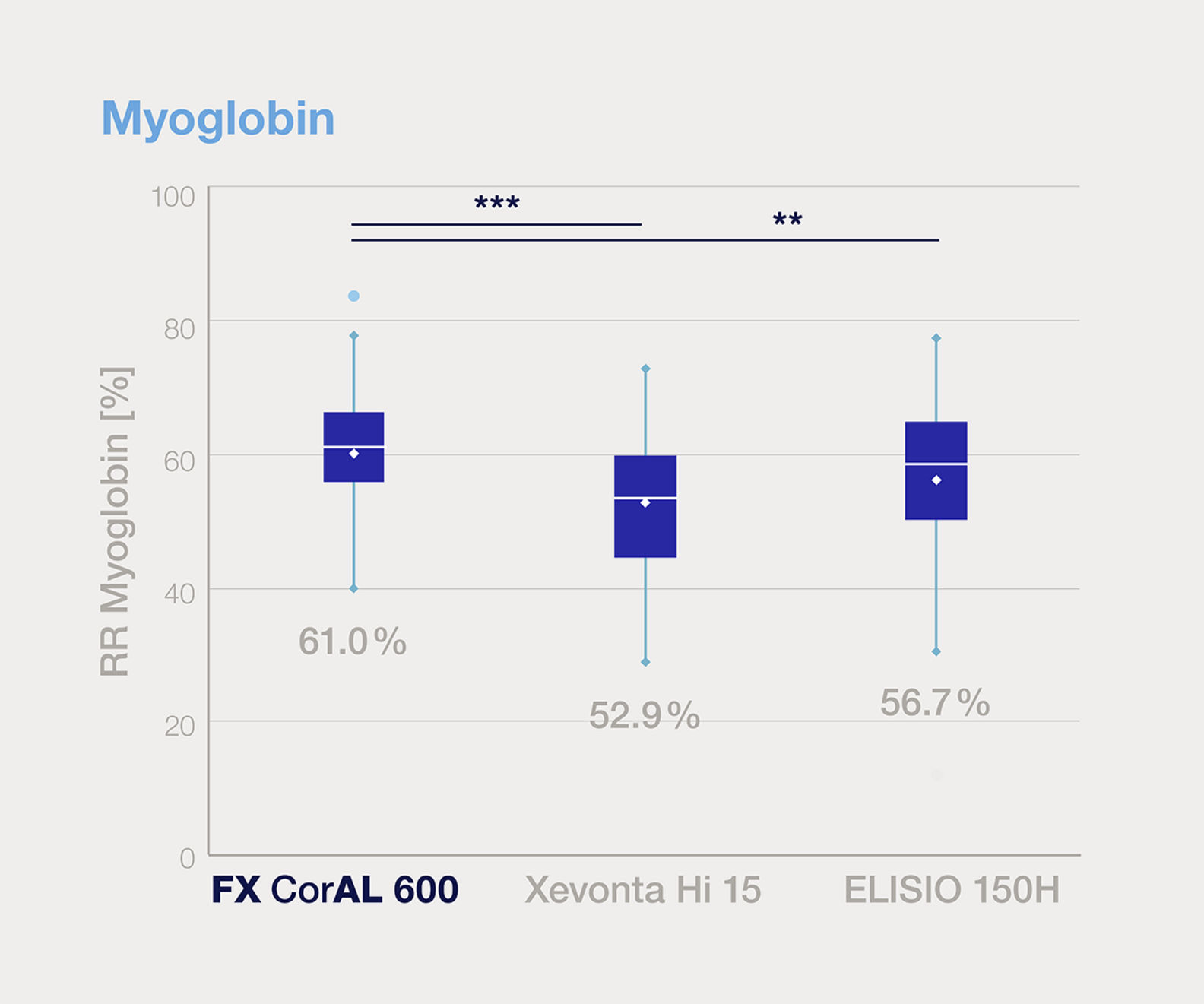
Dialysers investigated in this study: FX CorAL 600 / 80 (Fresenius Medical Care); FX CorDiax 600 / 80 (Fresenius Medical Care); xevontaHi 15 / 20 (B. Braun); Polyflux 140 H /170 H (Baxter); ELISIO™-15H /19H (Nipro); FDX-150GW / 210GW (Nikkiso Medical); THERANOVA 400 (Baxter); SUREFLUX™-15UX /19UX (Nipro).
Effective middle molecules removal
Clinical evidence shows better removal rates of β2-microglobulin and myoglobulin for FX CorAL compared to reference dialysers during four hour high-voume HDF treatment.6
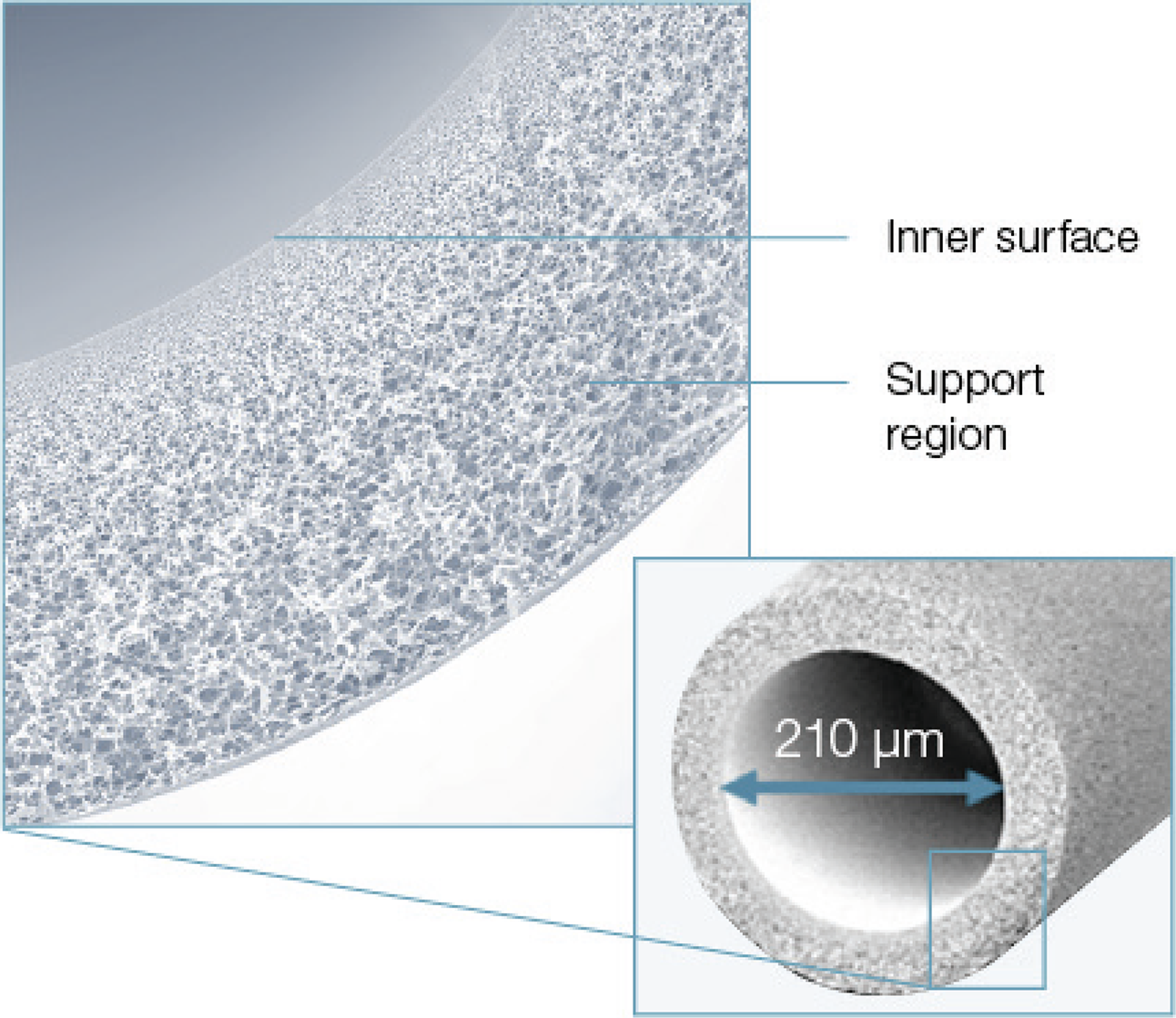
FX CorAL HDF Dialyser fiber
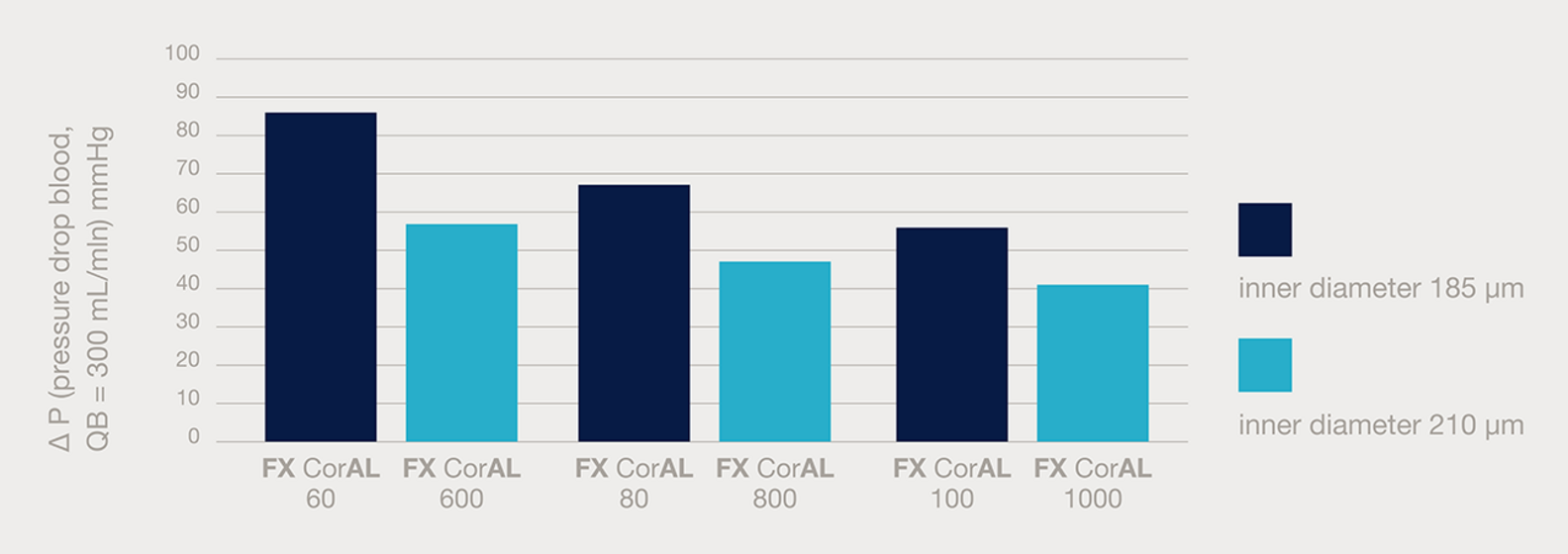
Fiber geometry to facilitate high subsitution volume
Study subgroup analysis showed an inverse relationship between convection volume and risk of mortality.8,24 According Basile et al., the recommended convection volume is the maximum possible, of at least 23 L. It is proposed that a convection volume of at least 23 L (for 1.73m2 body surface area) is suggested to enhance the clinical outcomes of HDF therapy. 25
- Increased inner diameter of 210 µm compared to 185 µm substantially reduces the pressure drop within the hollow fiber (according to the Hagan-Poiseuille law)26,27
- Lower flow resistance leads to a decrease in pressure drops which is proposed to cause less stress for the blood22
Learn more about FX CorAL
1 https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng107, Renal replacement therapy and conservative management, published date: October 2018.
* All statements and assessments by NICE are based on care practice and costs in England.
3 Internal calculation is based on an example at QB = 300 mL/min and a 240-minute treatment. There are savings of 34 L of dialysis fluid with post HDF at AutoFlow factor 1.2, with QD = 360 mL/min, compared to post HDF, with a fixed QD = 500 mL/min.
4 Marcelli, D. et al., High-Volume Postdilution Hemodiafiltration Is a Feasible Option in Routine Clinical Practice, Artificial Organs 2015, 39(2): 142–149.
5 Moustapha et al, (2020) Manual Individualization of the Dialysate Flow According to Blood Flow: Effects on the Hemodialysis Dose Delivered and on Dialysate Consumption. J Kidney 6:181. doi-10.35248/2472-1220.20.6.181.
6 Ehlerding, G. et al., Randomized comparison of three high-flux dialyzers during high volume online hemodiafiltration – the comPERFORM study, Clin Kidney J 2021 Oct 5;15(4):672-680. https://doi.org/10.1093/ckj/sfab196
7 Krick G, Ronco C (eds): On- Line Hemodiafiltration: The Journey and the Vision. Contrib Nephrol. Basel, Karger, 2011, vol 175, pp 170–185.
8 Maduell F. et al., High-efficiency postdilution online hemodiafiltration reduces all-cause mortality in hemodialysis patients, Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (2013); 24: 487-497.
10 Pedrini, L. et al., Long-term effects of high-efficiency on-line haemodiafiltration on uraemic toxicity. A multicentre prospective randomized study, Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation (2011); 26: 2617-2624.
11 Ok E., et al., Mortality and cardiovascular events in online haemodiafiltration (OL-HDF) compared with high-flux dialysis: results from the Turkish OL-HDF Study, Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation (2013); 28: 192-202.
12 Hornig C. et al., Switching from high-flux dialysis to hemodiafiltration: Cost-consequences for patients, providers, and payers. Semin Dial. 2022
14 NICE, Renal replacement therapy and conservative management; NICE guideline. 2018: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng107/chapter/Recommendations#.
15 NICE, RRT and conservative management; Cost-effectiveness analysis: HDF versus high flux HD. 2018: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng107/evidence/costeffectiveness-
16 NICE, RRT and conservative management; Modalities of RRT. 2018: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng107/evidence/b-modalities-of-rrt-pdf-6542344047.
17 Canaud, B. et al., Hemodiafiltration to Address Unmet Medical Needs ESKD Patients, Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 13: 1435–1443, 2018.
18 Maduel, F. et al., Impact of the 5008 monitor software update on total convective volume, Nefrologia (English Version) 2014; 34: 599–604.
19 Imamović G. et al., Principles of Haemodiafiltration: Rationale for Improved Patients’ Survival. Advances in Hemodiafiltration. InTech; 2016, Chapter 2. dx.doi.org/10.5772/63067
20 Marcelli, D. et al., Modifiable factors associated with achievement of high-volume post-dilution hemodiafiltration: results from an international study, Int J Artif Organs 2015; 38 (5): 244–250.
21 Ying I, Levitt Z, Jassal SV. Should an elderly patient with stage V CKD and dementia be started on dialysis? Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014 May;9(5):971-7. doi: 10.2215/CJN.05870513.
22 Lang T. et.al., Hemodiafiltration: Technical and Medical Insights. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Jan 21;10(2):145.
23 Melchior, P. et al., Complement activation by dialysis membranes and its association with secondary membrane formation and surface charge. Artif Organs 2021 Jul;45(7):770-778 https://doi.org/10.1111/aor.13887
24 Peters et al., Haemodiafiltration and mortality in end-stage kidney disease patients: a pooled individual participant data analysis from four randomized controlled trials Nephrol Dial Transplant (2016) 31: 978–984
25 Basile, C. et al., Why choose high volume online post-dilution hemodiafiltration? J Nephrol 30, 181–186 (2017).
26 FX CorDiaxHDF, Haemodiafilter Instructions for Use.
27 FX CorDiax, High-Flux Dialysers. Instructions for Use.
28 Penne et al., Short-term effects of online hemodiafiltration on phosphate control: a result from the randomized controlled Convective Transport Study (CONTRAST) Am J Kidney Dis 2010 Jan;55(1):77-87.