High-volume hemodiafiltration treatment can reduce mortality rates2
The latest CONVINCE study reinforces our original conviction: every patient should get the chance to benefit from HighVolumeHDF

Effect of Hemodiafiltration (HDF) or Hemodialysis (HD) on Mortality in Kidney Failure
Blankestijn PJ, Vernooij RWM, Hockham C, Strippoli GFM, Canaud B, Hegbrant J, Barth C, Covic A, Cromm K, Cucui A, Davenport A, Rose M, Török M, Woodward M, Bots ML; for the CONVINCE Scientific Committee Investigators.
N Engl J Med 2023 Aug 24;389(8):700-709.
Study Design and Methods
Aim: To investigate whether high-dose HDF offers survival benefits as compared with conventional high-flux HD.
Patients: 1360 patients from 61 dialysis centers in eight European countries, treated with high-flux HD, and deemed to be candidates for a convection volume of at least 23 L per session.
Design: A pragmatic, 1:1 randomised controlled trial with outcomes assessed over 30 months (median). 683 patients were assigned to online high-volume HDF and 677 patients to high-flux HD. High-volume HDF means post-dilution HDF with online production of fluids and convection volume ≥ 23 L per session.
Method: Convection volume targets achieved with stepwise adjustment over 2-3 weeks; interventions and outcomes assessed over 30 months (median)
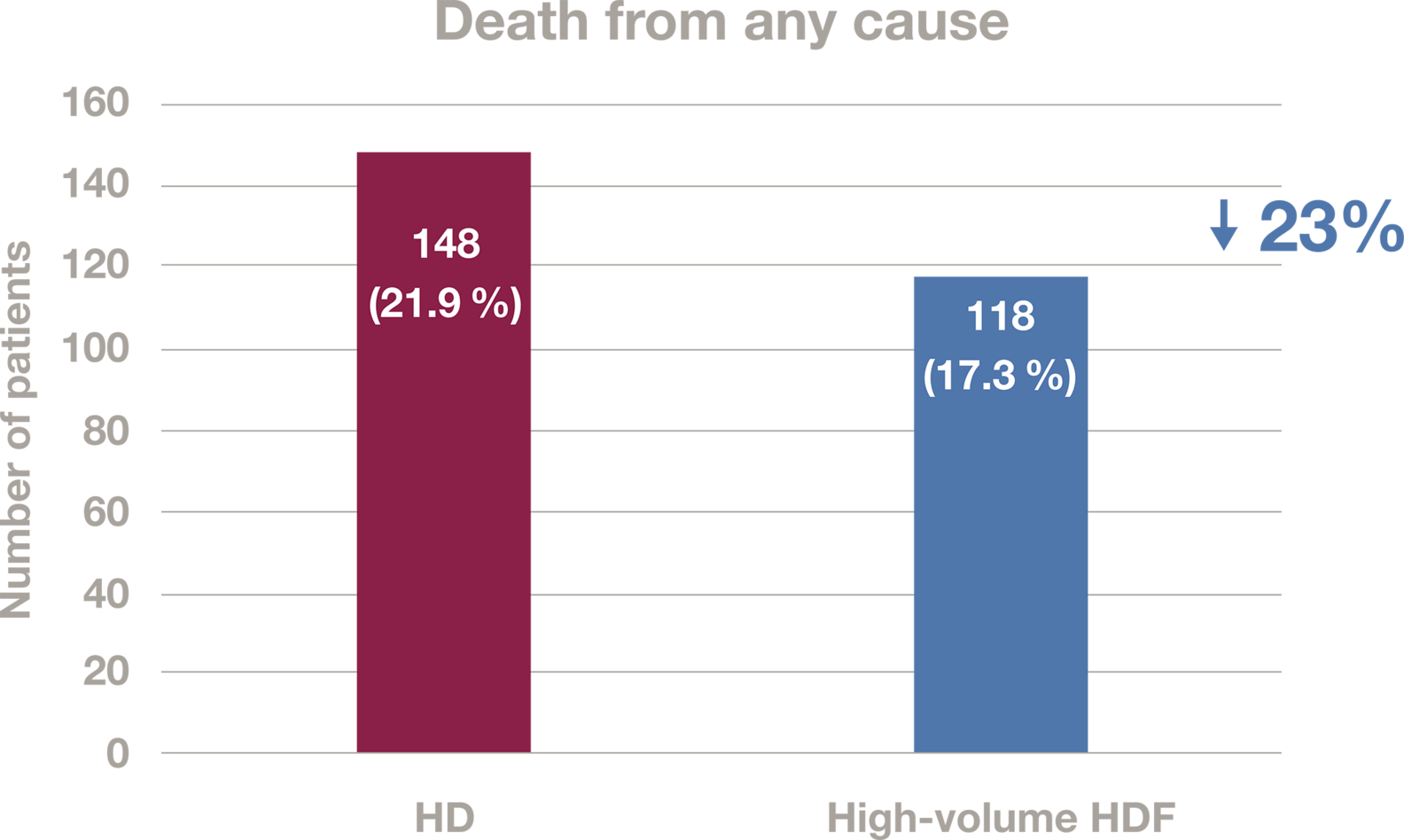
Primary outcome: Death from any cause.
Secondary outcome: Key secondary outcomes were cause-specific mortality, composite of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, kidney transplantation, and recurrent hospitalisations for any cause and for causes related to infection
Results
Primary outcome:
Death from any cause occurred in 118 patients (17.3%) in the HDF group and in 148 patients (21.9%) in the HD group. Patients in the HDF group had a 23% lower rate of mortality (hazard ratio (HR), 0.77; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.65- 0.93; P = 0.005).
Secondary outcome:
- The risk of death from cardiovascular causes and the composite outcome of fatal or nonfatal cardiovascular outcomes were similar in the HDF and the HD group; with a reduction of infection-related death in favor of high-dose HDF, including from Covid-19 (HR, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.49 to 0.96).
- The Kt/V value over the course of the trial was higher in the HDF group than in the HD group (1.74 vs. 1.65).
- The target convection volume of at least 23 L was achieved in 92% of delivered HDF sessions, with a stable mean convection volume of 25.3 L over the course of the trial.
Conclusions
The CONVINCE study found a lower risk of death from any cause in patients receiving high-volume HDF than among patients receiving high-flux HD. Infection-related and cardiovascular deaths showed a suggestion of benefit for HDF although drawing such conclusions is complicated because Covid-19 as a diagnosis was added during the course of the trail. The study differs from previous studies in that it enrolled patients who were likely candidates for high-dose HDF nearly all the time. It did not identify an association between failure to achieve the high-dose target and any particular patient characteristic or vascular access type. The trial results support the evidence that high-volume HDF can result in a clinically important survival benefit.
download CONVINCE trial summary