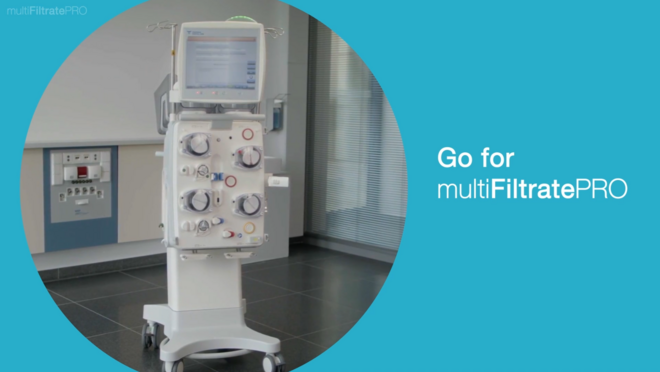
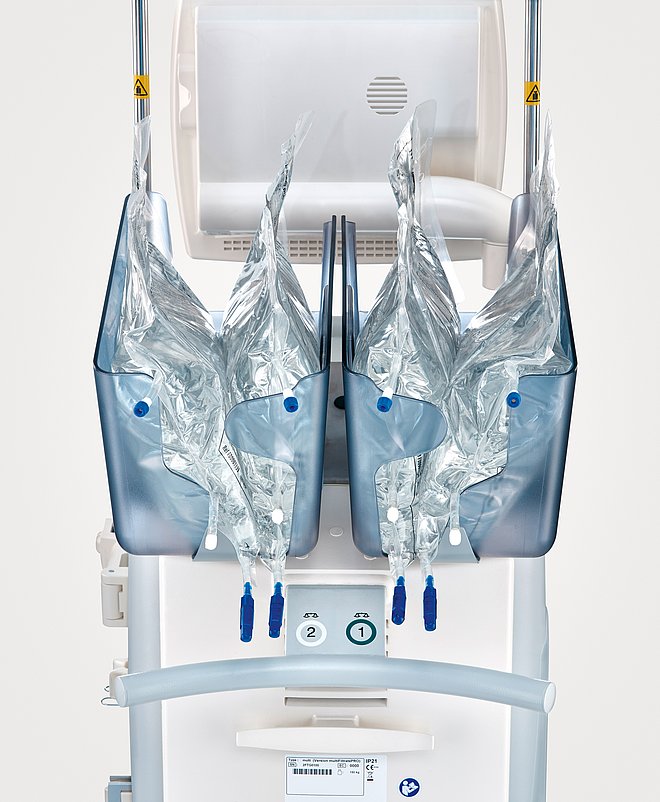
Integrating Ci‑Ca therapy in your clinical practice
Ci‑Ca therapy is a continuous kidney replacement therapy method that was developed by Fresenius Medical Care together with experienced clinicians. It was designed to provide reliable regional anticoagulation, using machine integrated citrate and calcium management.
Your professional world is changing constantly. You appreciate technologies that are continuously evolving and help you to provide your patients with even better therapy. We would like to support you by offering a comprehensive approach for citrate anticoagulation-based CKRT: Ci‑Ca therapy.
At a time when healthcare professionals are increasingly involved in non-caregiving activities such as administration, treatment documentation and medication preparation, there is a growing need for reliable, one-stop solutions which decrease the strain on the ICU staff.
Fresenius Medical Care is the first provider to offer a complete range of Ci‑Ca therapy products from a single source, supporting healthcare professionals to focus on the essential: patient care.
Regional citrate anticoagulation enables patient treatment with less bleeding complications and less filter clotting compared to heparin CKRT.1‑3 Ci-Ca therapy is one option for implementing regional citrate anticoagulation; it is an effective and reliable alternative to heparin4‑11 and lets your ICU staff focus more on the patient and less on handling issues.5,11
The prescribing information for Calrecia can be found here.
The prescribing information for Cifoban can be found here.
Participate in our experience: Fresenius Medical Care was the first to offer a completely machine integrated Ci‑Ca regional citrate anticoagulation. Healthcare professionals in more than 30 countries have already gained experience with Ci‑Ca therapy and appreciate its reliable application in clinical routines.5,6
Our proven citrate protocol is fully integrated in the multiFiltratePRO and reflected in all our Ci‑Ca products.
ICU days are busy and, as a doctor, you need to stay in control of a very complex environment. You shouldn’t need to worry about the reliability of CKRT treatments. Ci-Ca therapy supports excellent patient treatment with few clotting and bleeding complications.5‑8,13,14

Your question
What is the advantage of Ci‑Ca therapy
over standard heparin treatment?
Our answer
Citrate anticoagulation-based CKRT enables excellent patient treatment with fewer bleeding complications and less filter clotting compared to heparin.3,12‑14 Ci‑Ca regional anticoagulation is an effective and reliable alternative to heparin:
- Proven citrate protocol5‑8
- Enabling adherence to KDIGO AKI guideline2
- Low associated bleeding risk5,7,8
- Long filter patency4,6,8,10
- Ci-Ca anticoagulation may cause metabolic disorders5,6,7,8
- Citrate anticoagulation-based CKRT may not be suitable for patients with contraindications2
Nurses carry a lot of responsibility. So you look for ways to reduce workload and to focus on what is important. We help you to conduct a smoothly running CKRT with few interventions, making your work more plannable and enabling you to focus more on your patient.5,11

Your question
How can Ci‑Ca therapy give me more
plannability and reduce my workload?
Our answer
Compared to heparin anticoagulation, Ci‑Ca therapy reduces the number of nurse interventions, and facilitates efficient work planning:
- Prolonged filter lifetime corresponds to fewer filter changes4,10
- Low bleeding risk with expectedly fewer interventions needed5,7,8
- Ci‑Ca Therapy protocol and products support a predictable workflow5,11
Regular observations are still required during Ci-Ca therapy due to the associated risks.
Budget decisions come with a lot of responsibility. You want to make sure that your clinic is offering the best possible treatment while managing your budget wisely. We strive to limit total cost of ownership while conducting advanced therapies.

Your question
How does Ci‑Ca therapy support a value‑based
approach and help to meet budget requirements?
Our answer
Although Ci-Ca therapy has additional associated costs due to the required solutions, Ci-Ca therapy may improve your CKRT cost structure and total cost of ownership compared to systemic anticoagulation:5,15
- Fewer bleeding events, potentially resulting in a lower number of required blood transfusions5,16
- Less filter clotting leads to fewer treatment interruptions, reducing the workload and increasing the plannability of tasks4,5,10,11
- The smart Ci‑Ca protocol enables efficient consumption of fluids by avoiding relevant predilution17,18
Managing care is a complex task. You need to consider many different aspects – from therapy optimization to processes and costs. We offer you a one-stop solution from a strong and reliable partner.

Your question
What’s the benefit for our hospital
when switching to Ci‑Ca therapy?
Our answer
Fresenius Medical Care can be your trusted one-stop business partner:
- With our comprehensive Ci‑Ca therapy portfolio of tailored products and services, we offer what you need for a reliable and effective CKRT4‑8,10,11 from a single source.
- As the world's leading provider of products and services for individuals with kidney diseases, we are able to provide the full range of support required for switching to Ci‑Ca therapy as well as for daily operation.
1 Tsujimoto H et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020; 12(12):CD012467
2 KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury., Kidney Int Suppl 2012; 2:1‑138
3 Bai M et al. Intensive Care Med 2015; 41:2098‑2110
4 Bianchi NA et al. Blood Purif 2020; 49:567‑575
5 Kalb R et al. Ther Apher Dial 2013; 17:202‑212
6 Morgera et al. Crit Care Med 2009;37:2018‑2024
7 Slowinski T et al. Crit Care 2015; 19:349
8 Link A et al. Crit Care 2012; 16:R97
9 Huguet M et al. Int J Artif Organs 2017; 40:676‑682
10 Hafner S et al. J Intensive Care 2015; 3:35
11 Houllé-Veyssière et al. Intensive Crit Care Nurs 2016; 36:35‑41
12 Hetzel GR et al. Nephrol Dial Transpl 2011; 26:232‑239
13 Zarbock A et al. JAMA 2020; 324:1629‑1639
14 Li L et al. Semin Dial 2021; 34:209‑217
15 Dalhuisen A et al. Neth J Crit Care 2017; 25:122‑127
16 Kindgen-Milles D et al. Curr Opin Crit Care 2018; 24:450‑454
17 Huang Z et al. Int J Artif Organs 2008, 31:525‑534
18 Nalesso F et al. J Clin Med 2020; 9:1529


![[Translate to English (GB):] Think partner](/fileadmin/data/masterContent/images/Critical_Care/square_partner.png)