Therapeutic apheresis
Removing harmful substances
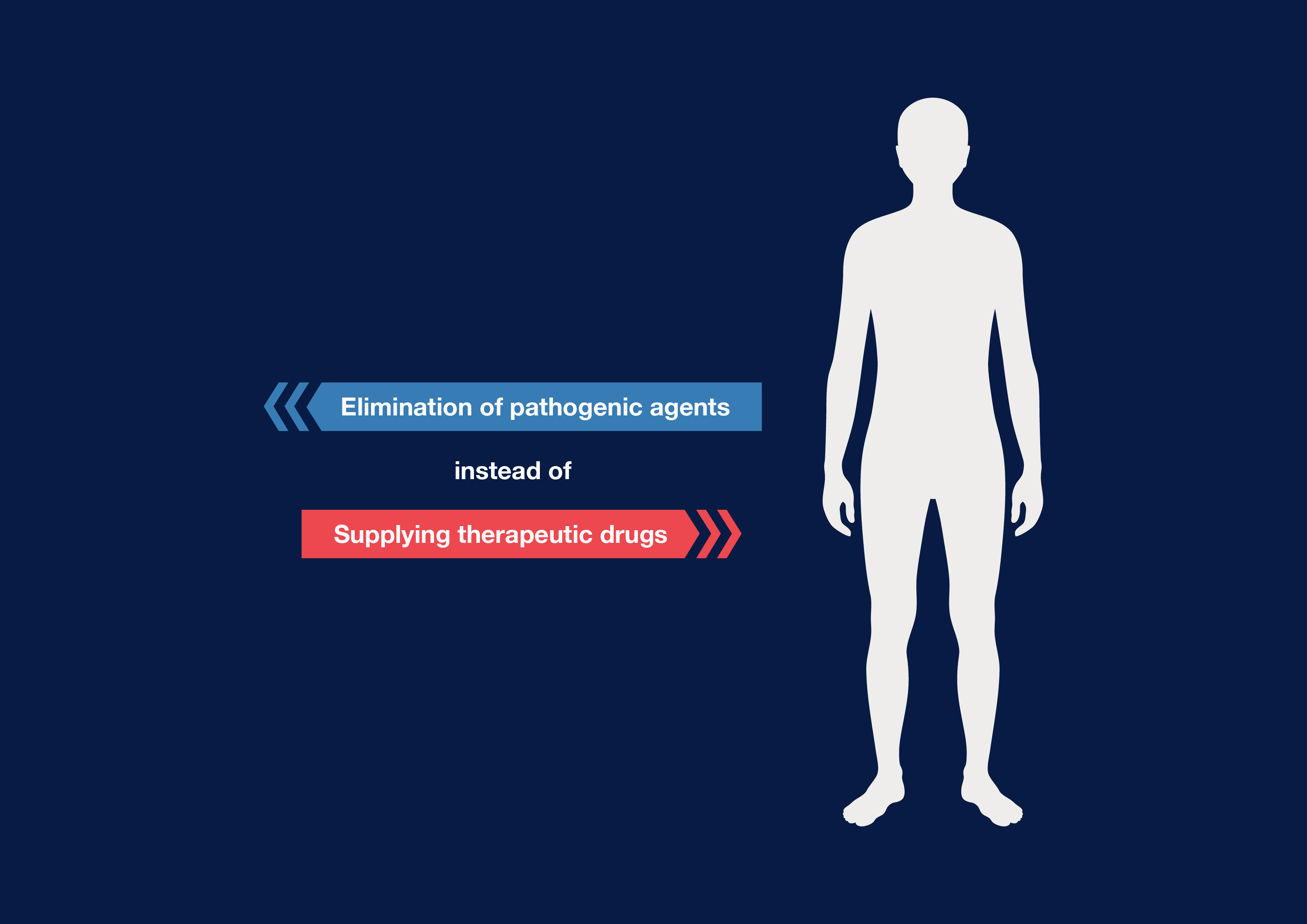
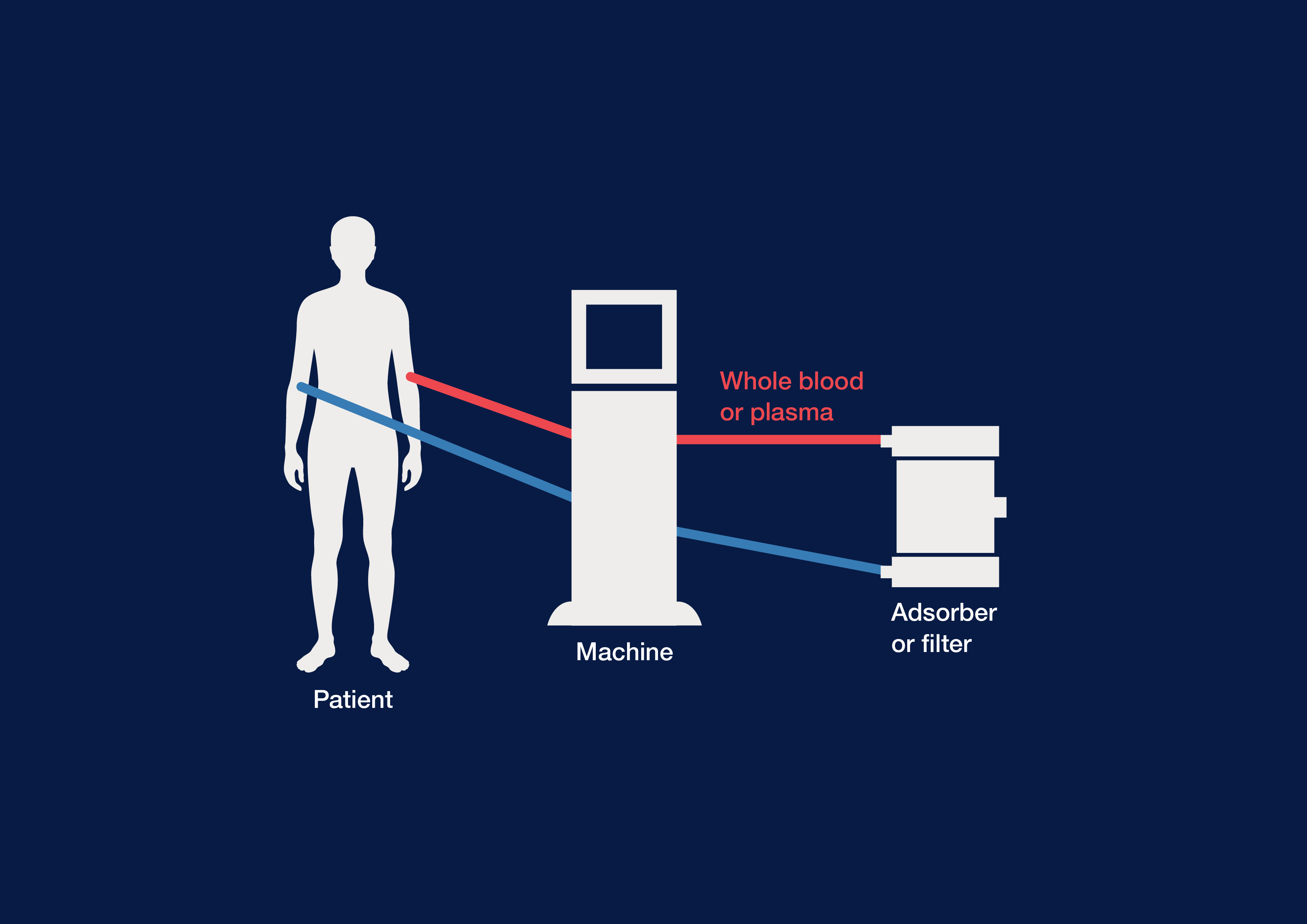
Therapeutic apheresis is an extracorporeal blood purification procedure. Its working principle is the selective or semi-selective removal of pathogenic components from the patient's blood or plasma and not the administration of therapeutic drugs. The blood is returned to the patient’s body immediately after purification.
Therapeutic apheresis yields benefits in a variety of medical conditions, including metabolic disorders, organ transplantation and autoimmune diseases. Therapy application can range from acute organ support to more preventive measures that alleviate signs and symptoms of disease and enable protection against critical progression.
Immunoadsorption
Immunoadsorption therapy removes specific antibodies from the blood plasma. Due to its high selectivity, it can treat a wide range of severe autoantibody mediated clinical indications such as myasthenia gravis, steroid-refractory relapse in multiple sclerosis, certain settings of solid organ rejection, idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy or certain very rare diseases like pemphigus vulgaris where decision making should be individualized.1
Lipoprotein apheresis
Lipoprotein apheresis aims to substantially reduce high cholesterol levels and other harmful lipoproteins in the patient’s bloodstream and serves patients with homozygous FH or other forms of hypercholesterolemia, dyslipidemia and cardiovascular disease. Some of the lipoprotein apheresis devices also can be used for rheopheresis. Rheopheresis is an extracorporeal therapeutic apheresis procedure used to decrease blood viscosity and improve microperfusion by filtering rheologically relevant macromolecules out of the plasma.1
Therapeutic apheresis includes a variety of medical techniques, such as therapeutic plasma exchange or the adsorption of specific plasma components.
Thanks to our adsorbers, filters and many years of experience with extracorporeal methods, Fresenius Medical Care provides high-quality and versatile therapeutic apheresis treatment options for a wide range of diseases and disorders.
What is
therapeutic apheresis?
Watch to learn more.
1 Padmanabhan A et al. J Clin Apher 2019; 34:171-354